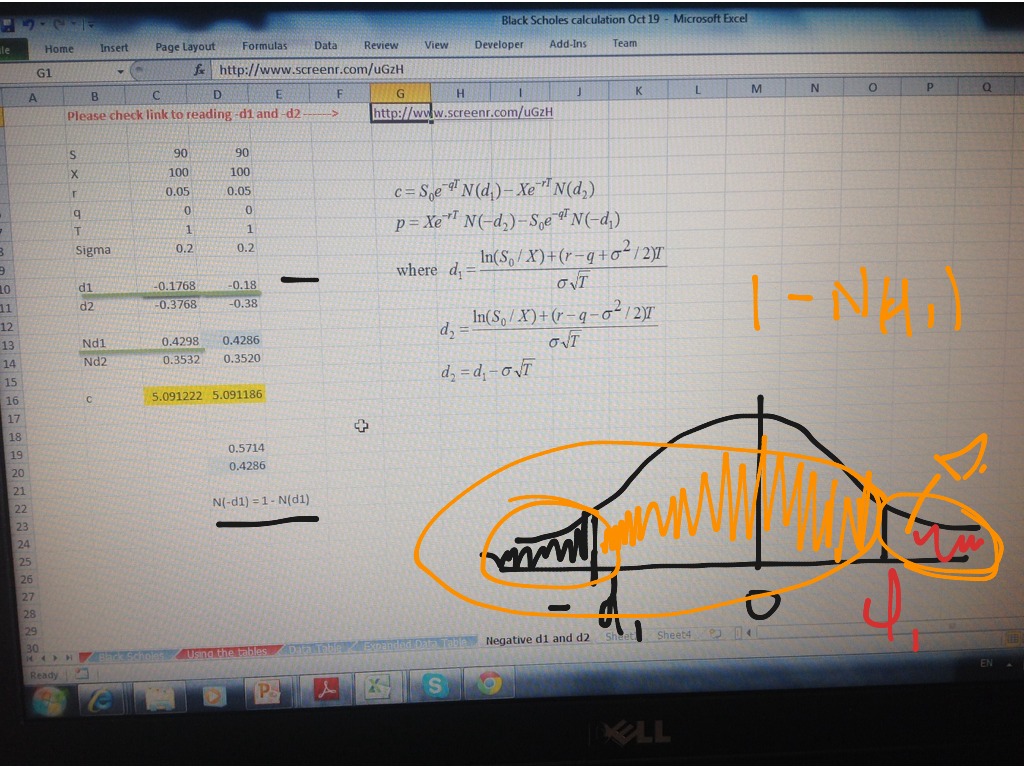
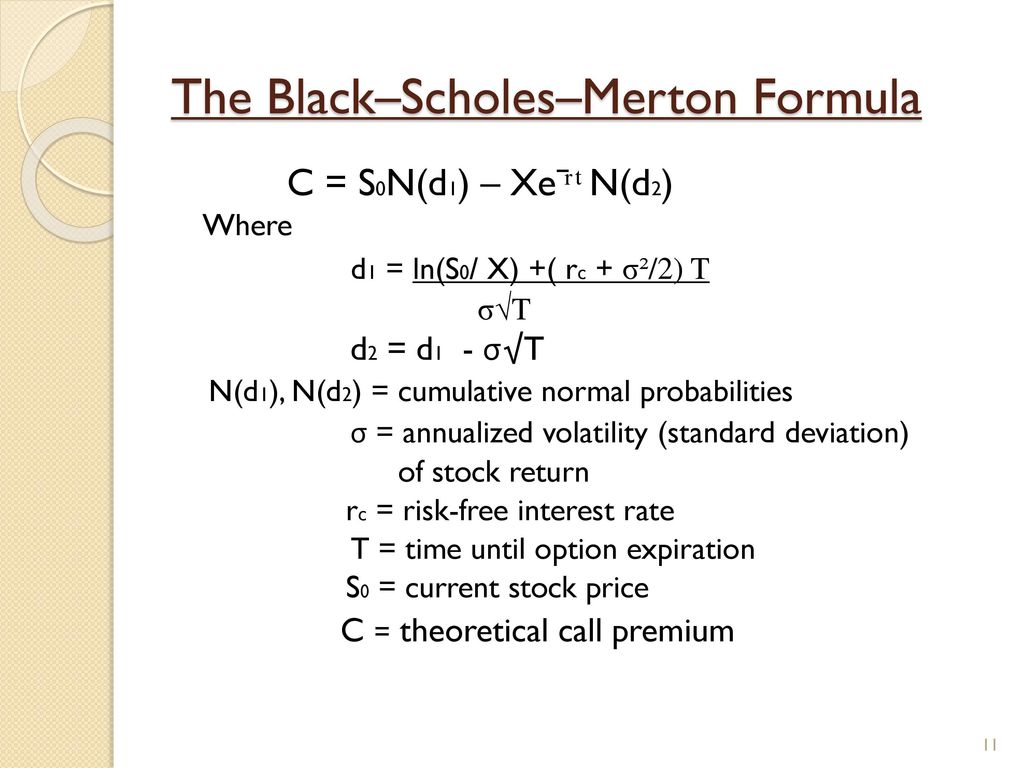
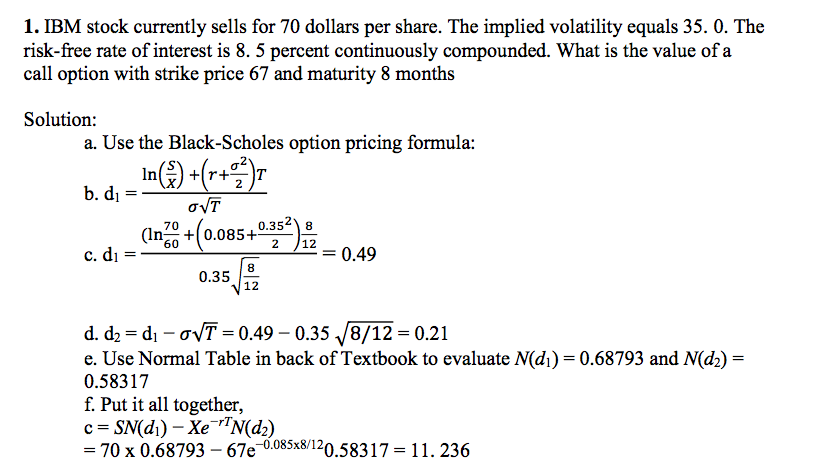
In the black scholes formula how can N(d1) represent the expected return in the event of an exercise and at the same time also mean 'delta' - probability that the option will

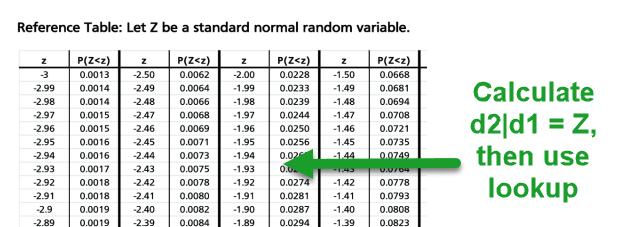
Consider a 1-year option with exercise price $60 on a stock with annual standard deviation 20%. The T-bill rate is 3% per year. Find N(d1) for stock prices $55, $60, and $65. (

Different approach to Black Scholes model and validation of dynamic delta hedging with Monte Carlo simulation - The Global Treasurer
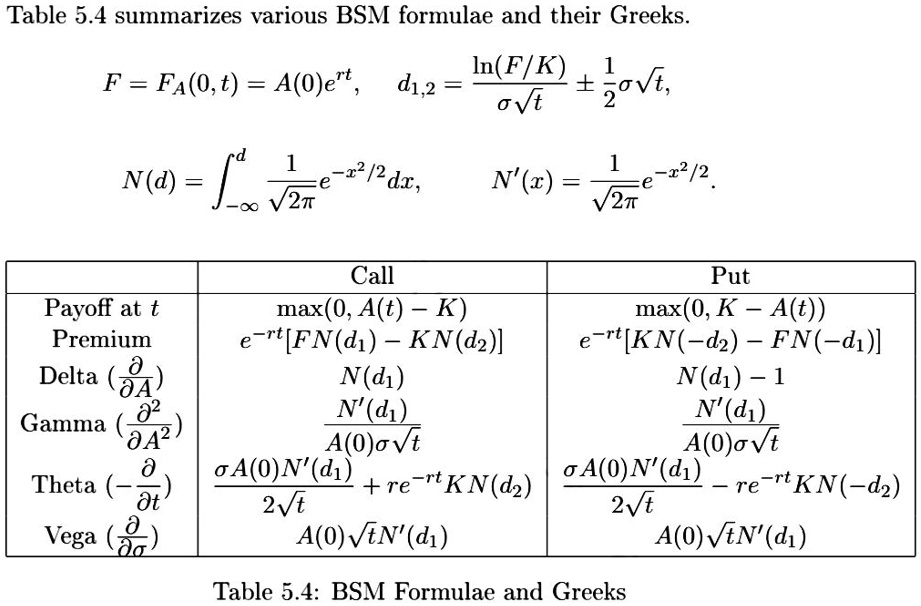
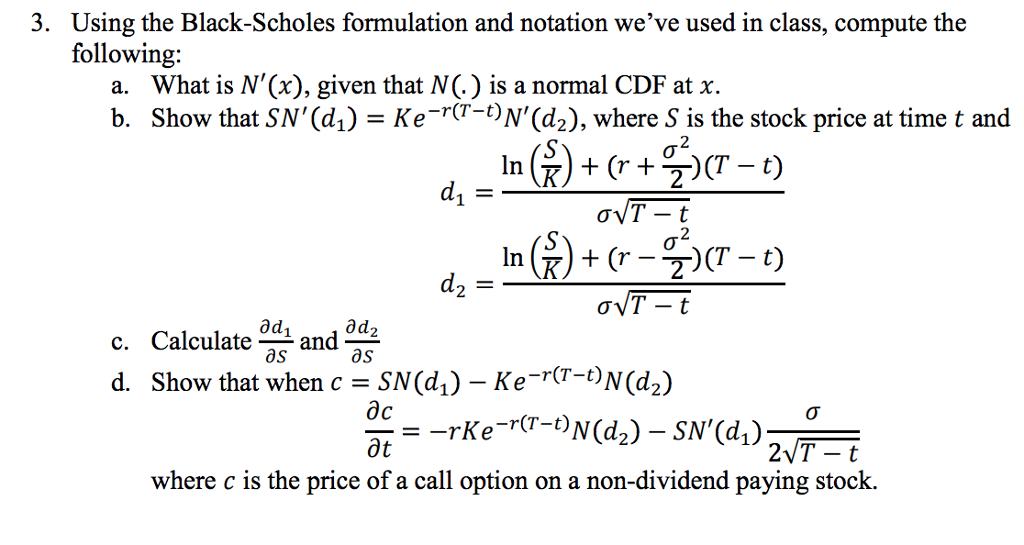
SOLVED: Table 5.4 summarizes various BSM formulas and their Greeks: In(FIK) F = FA(0,t) = A(0)e^(-rt), d1,2 = (ln(F/A(0)) + (r + 0.5 * σ^2)t) / (σ√t) N(d) = (1/√(2π)) ∫e^(-x^2/2)dx from -

SOLVED: We denote by r > 0 the risk-free interest rate. Recall the Black-Scholes model and the Black-Scholes formula for a T-expiry; K-strike European call option written on S having positive constant

In the black scholes formula how can N(d1) represent the expected return in the event of an exercise and at the same time also mean 'delta' - probability that the option will